Introduction
Loguytren problems, often associated with the hand’s connective tissue, can significantly impact daily activities. Although many people have heard the term, few understand the full scope of what dealing with loguytren problems truly entails. This condition, typically progressive, can cause discomfort, deformity, and challenges with hand function. Early diagnosis and proper treatment are crucial for managing symptoms effectively and maintaining quality of life. In this article, we will explore everything you need to know about loguytren problems, including causes, symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options, helping you stay informed and prepared.
What Are Loguytren Problems?
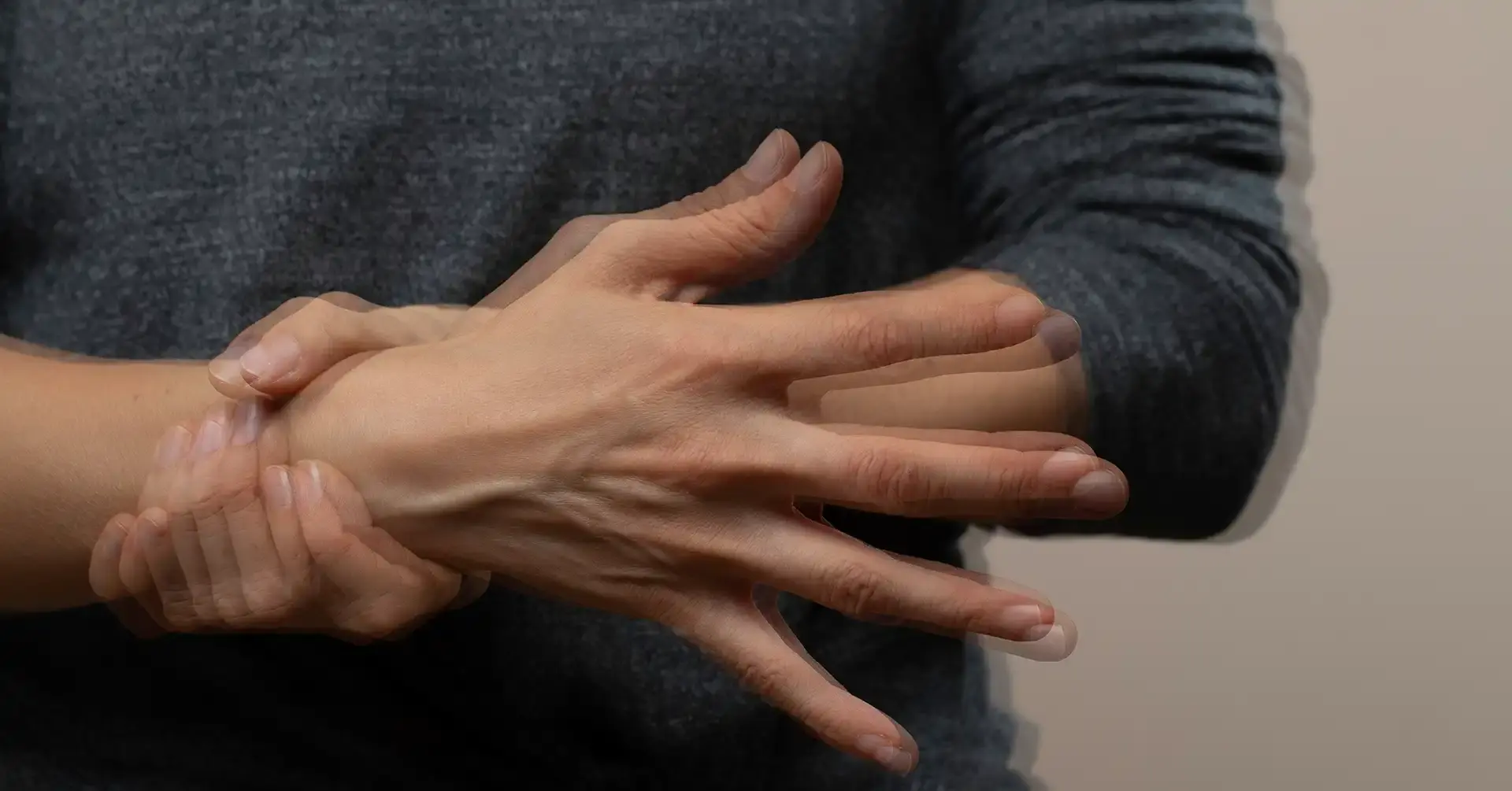
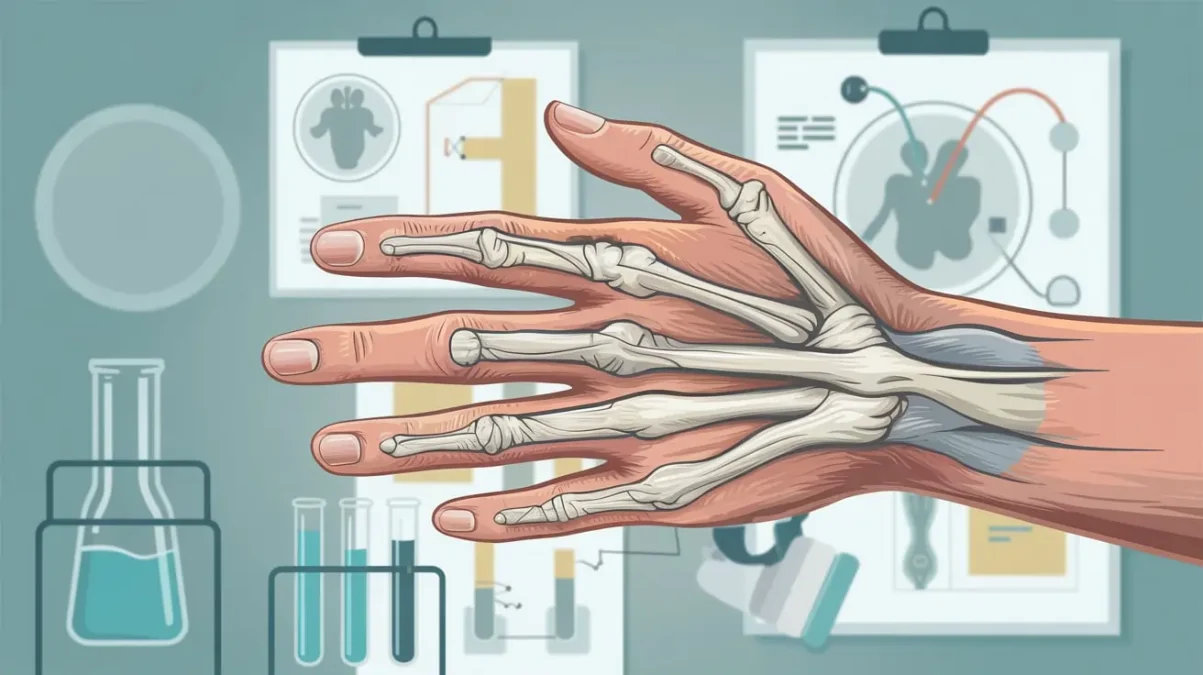
Loguytren problems refer to a thickening of the connective tissue under the skin of the palm and fingers. Over time, this thickening can develop into firm knots or cords that pull one or more fingers into a bent position. While it is usually painless, the inability to straighten the fingers completely can interfere with everyday tasks like shaking hands, grasping objects, or putting hands into pockets.
This condition most commonly affects the ring and little fingers but can vary from person to person. It tends to develop slowly over years, and although it might seem minor at first, it can progress to serious functional impairment.
Causes of Loguytren Problems
The exact cause of loguytren problems remains unclear, but researchers believe it involves a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some of the primary causes and risk factors include:
-
Genetic predisposition: A family history of loguytren problems significantly increases your risk.
-
Age: It generally affects people over the age of 40.
-
Gender: Men are more likely to develop loguytren problems than women.
-
Ancestry: People of Northern European descent are at a higher risk.
-
Lifestyle factors: Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption have been linked to a higher risk.
-
Medical conditions: Diabetes and epilepsy are associated with an increased likelihood of developing loguytren problems.
Symptoms of Loguytren Problems
Recognizing the symptoms early can help slow the progression of loguytren problems. Common symptoms include:
-
Nodules in the palm: Small lumps that may be tender initially but often become painless.
-
Thickened skin: The skin on the palm may appear puckered or dimpled.
-
Formation of cords: Tough bands of tissue may develop under the skin.
-
Finger contractures: One or more fingers bend towards the palm and cannot be fully straightened.
Symptoms typically worsen over time, and the progression can vary from mild to severe.
Risk Factors of Loguytren Problems
Several factors contribute to the likelihood of developing loguytren problems:
-
Family history: Genetic factors play a significant role.
-
Ethnicity: More common among people of Northern European ancestry.
-
Health conditions: Diabetes, thyroid disease, and liver disease can increase risk.
-
Substance use: Smoking and drinking alcohol can contribute to the development and progression.
-
Medications: Certain medications like anticonvulsants have been linked to a higher risk.
Understanding these risk factors can lead to earlier recognition and treatment.
How Loguytren Problems Are Diagnosed
Diagnosing loguytren problems usually involves a physical examination. During the exam, a healthcare provider will:
-
Inspect your hands for signs of nodules, cords, and skin changes.
-
Assess finger mobility and flexibility.
-
Perform a “tabletop test,” where you attempt to place your hand flat on a table.
In rare cases, imaging studies like ultrasound or MRI may be ordered to assess the extent of tissue involvement, but usually, a physical exam suffices.
Treatment Options for Loguytren Problems
Several treatment options are available, depending on the severity of the condition:
Non-Surgical Treatments
-
Observation: If symptoms are mild, regular monitoring may be sufficient.
-
Stretching exercises: Helps maintain hand mobility in early stages.
-
Splinting: Although controversial, it might prevent worsening contractures.
-
Steroid injections: Can reduce inflammation and slow progression.
Surgical Treatments
-
Needle aponeurotomy: A minimally invasive procedure where a needle breaks the cords under the skin.
-
Enzyme injections: Collagenase clostridium histolyticum injections can dissolve the cords.
-
Open surgery (fasciotomy or fasciectomy): Recommended for severe cases, involving removal of the thickened tissue.
Choosing the right treatment depends on how far the disease has progressed and how much it interferes with daily life.
Living with Loguytren Problems
Adjusting to life with loguytren problems can be challenging, but manageable. Tips for coping include:
-
Physical therapy: Helps maintain mobility and strength.
-
Hand protection: Using padded gloves during heavy tasks can prevent injury.
-
Assistive devices: Specially designed tools can help with tasks like gripping or writing.
-
Routine check-ups: Regular monitoring can detect progression early.
Support groups and occupational therapy can also provide emotional and practical help.
Preventing Loguytren Problems
While there’s no guaranteed way to prevent loguytren problems, you can minimize your risk through:
-
Healthy lifestyle: Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption.
-
Manage chronic conditions: Keeping diabetes and thyroid disorders under control can reduce your risk.
-
Hand care: Protect your hands from injury and repetitive strain.
Early detection and proactive care are key to managing the condition effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What are the early signs of loguytren problems?
The earliest signs often include small, tender nodules in the palm. Over time, the skin may become dimpled, and cords may form beneath the surface.
Is loguytren disease painful?
Usually, it is not painful. However, some people experience tenderness or discomfort, especially in the early stages.
Who is most at risk for loguytren problems?
Men over 40 of Northern European descent with a family history of the condition are at the highest risk.
Can loguytren problems go away on their own?
No, it typically worsens over time without treatment. Early intervention can slow progression but not reverse it.
How is loguytren different from arthritis?
Arthritis affects the joints, causing inflammation and pain. Loguytren affects the connective tissue beneath the skin, leading to finger contractures.
Are there non-surgical treatments for loguytren problems?
Yes, mild cases can be managed with stretching, splinting, and steroid injections.
When should surgery be considered?
Surgery is considered when contractures interfere significantly with hand function.
How effective is enzyme injection treatment?
Enzyme injections are effective for many people, offering a less invasive alternative to surgery with quicker recovery times.
Can lifestyle changes prevent loguytren problems?
While you can’t fully prevent it, avoiding smoking, excessive alcohol, and managing health conditions can help lower your risk.
Is physical therapy necessary after surgery for loguytren problems?
Yes, physical therapy is crucial for regaining full hand function and preventing recurrence after surgery.
Conclusion
Loguytren problems, though sometimes misunderstood, are a significant condition that can impact hand functionality and quality of life. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options empowers individuals to take control early and manage the condition effectively. Whether through non-invasive therapies or surgical solutions, there are many ways to address loguytren problems and maintain a healthy, active lifestyle. Regular check-ups, lifestyle changes, and staying informed are the best tools for coping with this complex condition.